Medial epicondylitis (golfer’s elbow) and lateral epicondylitis (tennis elbow) are among the most common elbow pathologies affecting people aged between 40 and 50 years. Although epicondylitis is often a self-limiting and improves with conservative treatment, the condition can be difficult to eradicate. In a recent publication, the effectiveness of platelet-rich plasma (PRP) injections and ultrasound-guided percutaneous tenotomy (Tenex) for the treatment of medial or lateral epicondylitis was reviewed.
In this retrospective study by Boden et al., the team at Emory contacted 75 patients who underwent either a PRP injection or the Tenex procedure for tennis elbow or golfer’s elbow. Of these patients 62 of them responded and completed surveys assessing their level of pain and function.
Thirty-two patients had received a PRP injection and 30 patients had undergone a Tenex procedure. In both groups, the patients both demonstrated clinical and statistical improvement in pain and function without a significant difference between the two groups.
This is one of the few studies comparing a partial tenotomy using the (Tenex device for the procedure) to another non-operative treatment for tennis and golfer’s elbow.
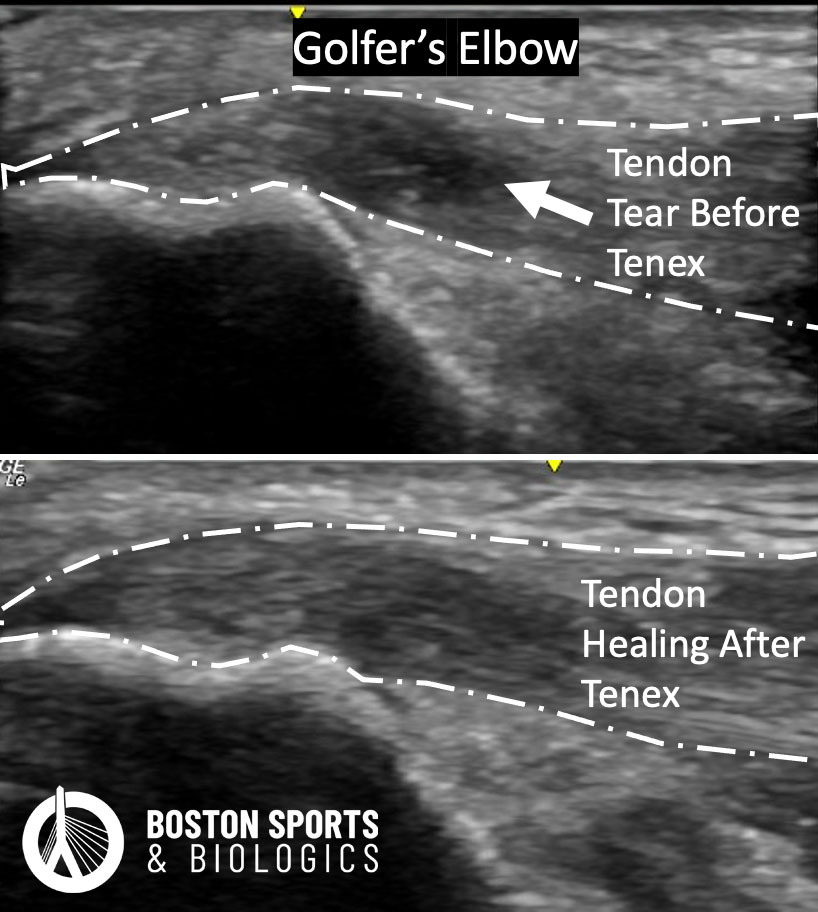
Tenex has been studied for refractory lateral epicondylitis and demonstrated a significant improvement in pain and function. In a study following patient for up to 3 years after the procedure patients still had continued improvement for up to 3 years after the procedure, with no tendon ruptures, infections or other complications (Chalian et al, 2021). In two other studies, the minimally invasive tenotomy demonstrated evidence of tissue healing in response to the procedure on follow-up ultrasound imaging (Seng et al, 2016; Ang et al, 2021).
Is stem cell therapy better than cortisone for knee arthritis? Learn the differences, risks, benefits, and long-term results of cortisone vs stem cell knee injections.
Read More