Ankle sprains are one of the most common
musculoskeletal injuries in people of all ages with at least >300,000
injuries per year in the United States [Nelson et al, 2007].
The ankle joint comprises the talocrural joint (between the tibia, fibula, and talus) and the subtalar joint (between the talus and calcaneus). The ankle joint is surrounded by ligaments that help stabilize the joint.
The lateral ligaments stabilize the ankle against inversion forces where the foot rolls inward, while the deltoid ligament on the medial side resists eversion [Hertel, 2002; Safran et al, 1999].
An ankle sprain occurs when these ligaments are stretched beyond the normal range of motion. Most sprains involve the ligaments on the outside of the ankle and are minor, but in more severe cases the ligaments can be torn leading to joint instability.
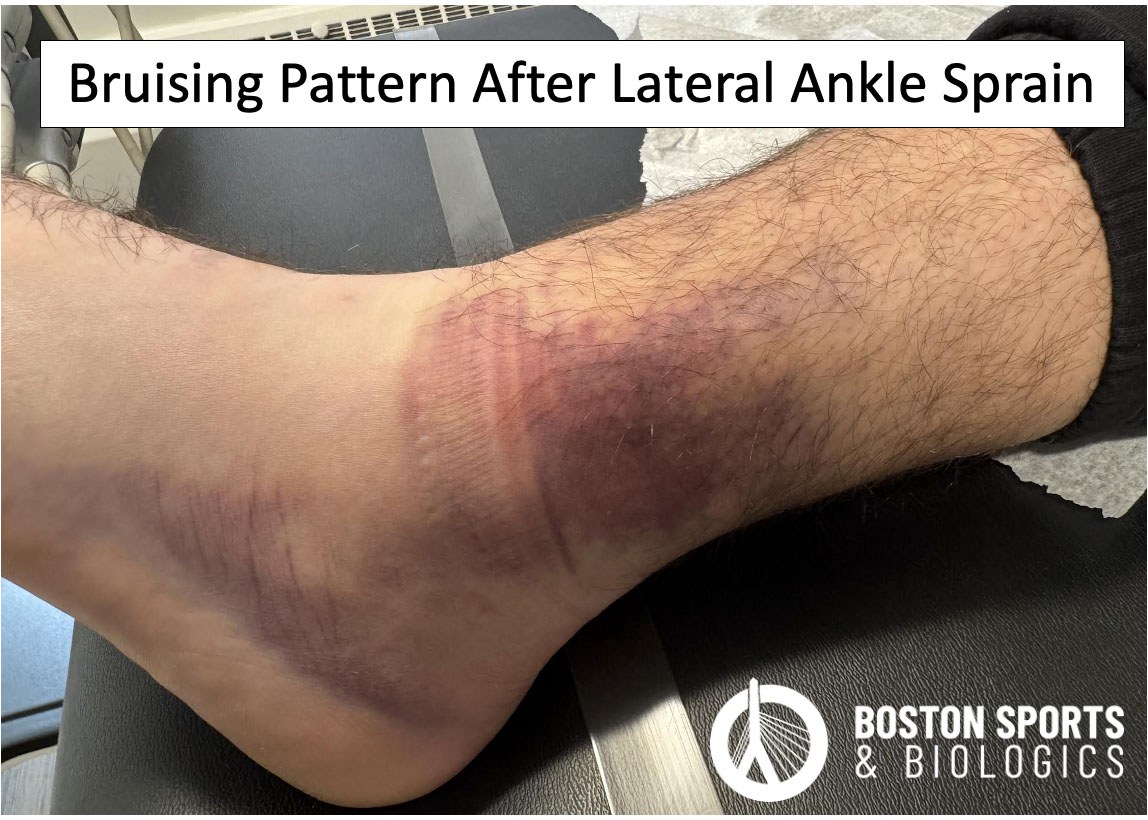
The symptoms of an ankle sprain vary depending on the grade of severity and the specific ligaments involved. Symptoms for acute ankle sprains include swelling and bruising around the ankle, pain, tenderness, decreased range of motion and difficulty walking.
Chronic ankle sprains are characterized by persistent symptoms and functional deficits following repeated injuries to the ankle ligaments and can result in chronic ankle instability. Up to 40% of individuals with an lateral ankle sprain develop symptoms of a chronic ankle sprain and instability [Hertel & Corbett, 2019; Herzog et al, 2019]. Repeated injuries and chronic instability can lead to degenerative changes in the ankle joint, with up to 78% of cases progressing to post-traumatic osteoarthritis [Owoeye et al, 2023; Wikstrom et al, 2013].
Diagnosis is based on detailed history, physical examination, and imaging. Certain physical tests may be utilized to reproduce symptoms and measure range of motion at time of exam.
Conservative Management
Initial treatment of acute ankle sprains consists of immediate care (rest, ice, NSAIDs, bracing) and physical therapy for functional rehabilitation [Kaminski et al, 2013].
Platelet Rich Plasma (PRP) Injections
PRP concentrates a patient’s blood to increase various growth factors. The outcomes of platelet-rich plasma (PRP) injections for treating ankle sprains have been evaluated in several studies. PRP injections may offer short-term benefits in pain reduction and functional improvement with faster return to sport for acute ankle sprains, but results regarding their efficacy have been mixed.
Surgical Intervention
Surgical options for treating ankle sprains primarily focus on addressing chronic lateral ankle instability, which can develop following acute ankle sprains that do not heal properly. Surgery may be necessary for more complex cases or chronic instability to reconstruct the injured ligament(s).
REFERENCES:
Alghadir AH, Iqbal ZA, Iqbal A, Ahmed H, Ramteke SU. Effect of Chronic Ankle Sprain on Pain, Range of Motion, Proprioception, and Balance among Athletes. Int J Environ Res Public Health. 2020 Jul 23;17(15):5318.
Baltes TPA, Arnáiz J, Geertsema L, Geertsema C, D'Hooghe P, Kerkhoffs GMMJ, Tol JL. Diagnostic value of ultrasonography in acute lateral and syndesmotic ligamentous ankle injuries. Eur Radiol. 2021 Apr;31(4):2610-2620.
Cheng Y, Cai Y, Wang Y. Value of ultrasonography for detecting chronic injury of the lateral ligaments ofthe ankle joint compared with ultrasonography findings. Br J Radiol. 2014 Jan;87(1033):20130406.
Choi WS, Cho JH, Lee DH, Chung JY, Lim SM, Park YU. Prognostic factors of acute ankle sprain: Need for ultrasonography to predict prognosis. J Orthop Sci. 2020 Mar;25(2):303-309.
George J, Jaafar Z, Hairi IR, Hussein KH. The correlation between clinical and ultrasound evaluation of anterior talofibular ligament and calcaneofibular ligament tears in athletes. J Sports Med Phys Fitness. 2020 May;60(5):749-757.
Hertel J. Functional Anatomy, Pathomechanics, and Pathophysiology of Lateral Ankle Instability. J Athl Train. 2002 Dec;37(4):364-375.
Hertel J, Corbett RO. An Updated Model of Chronic Ankle Instability. J Athl Train. 2019 Jun;54(6):572-588.
Herzog MM, Kerr ZY, Marshall SW, Wikstrom EA. Epidemiology of Ankle Sprains and Chronic Ankle Instability. J Athl Train. 2019 Jun;54(6):603-610. doi: 10.4085/1062-6050-447-17. Epub 2019 May 28.
Holmes A, Delahunt E. Treatment of common deficits associated with chronic ankle instability. Sports Med. 2009;39(3):207-24.
Hosseinian SHS, Aminzadeh B, Rezaeian A, Jarahi L, Naeini AK, Jangjui P. Diagnostic Value of Ultrasound in Ankle Sprain. J Foot Ankle Surg. 2022 Mar-Apr;61(2):305-309.
How CH, Tan KJ. Doctor, I sprained my ankle. Singapore Med J. 2014 Oct;55(10):522-4; quiz 525.
Kaminski TW, Hertel J, Amendola N, Docherty CL, Dolan MG, Hopkins JT, Nussbaum E, Poppy W, Richie D; National Athletic Trainers' Association. National Athletic Trainers' Association position statement: conservative management and prevention of ankle sprains in athletes. J Athl Train. 2013 Jul-Aug;48(4):528-45.
Kemmochi M, Sasaki S, Fujisaki K, Oguri Y, Kotani A, Ichimura S. A new classification of anterior talofibular ligament injuries based on ultrasonography findings. J Orthop Sci. 2016 Nov;21(6):770-778.
Laver L, Carmont MR, McConkey MO, Palmanovich E, Yaacobi E, Mann G, Nyska M, Kots E, Mei-Dan O. Plasma rich in growth factors (PRGF) as a treatment for high ankle sprain in elite athletes: a randomized control trial. Knee Surg Sports Traumatol Arthrosc. 2015 Nov;23(11):3383-92.
Lee SH, Yun SJ. The feasibility of point-of-care ankle ultrasound examination in patients with recurrent ankle sprain and chronic ankle instability: Comparison with magnetic resonance imaging. Injury. 2017 Oct;48(10):2323-2328.
Nelson AJ, Collins CL, Yard EE, et al. Ankle injuries among United States high school sports athletes, 2005–2006. J Athl Train. 2007;42:381–387.
Owoeye OBA, Paz J, Emery CA. Injury severity at the time of sport-related ankle sprain is associated with symptoms and quality of life in young adults after 3-15 years. Ann Med. 2023;55(2):2292777.
Rowden A, Dominici P, D'Orazio J, Manur R, Deitch K, Simpson S, Kowalski MJ, Salzman M, Ngu D. Double-blind, Randomized, Placebo-controlled Study Evaluating the Use of Platelet-richPlasma Therapy (PRP) for Acute Ankle Sprains in the Emergency Department. J Emerg Med. 2015 Oct;49(4):546-51.
Safran MR, Benedetti RS, Bartolozzi AR 3rd, Mandelbaum BR. Lateral ankle sprains: a comprehensive review: part 1: etiology, pathoanatomy, histopathogenesis, and diagnosis. Med Sci SportsExerc. 1999 Jul;31(7 Suppl):S429-37.
Smith SE, Chang EY, Ha AS, Bartolotta RJ, Bucknor M, Chandra T, Chen KC, Gorbachova T, Khurana B, Klitzke AK, Lee KS, Mooar PA, Ross AB, Shih RD, Singer AD, Taljanovic MS, Thomas JM, Tynus KM, Kransdorf MJ. ACR Appropriateness Criteria® Acute Trauma to the Ankle. J Am Coll Radiol. 2020 Nov;17(11S):S355-S366.
Wikstrom EA, Hubbard-Turner T, McKeon PO. Understanding and treating lateral ankle sprains and their consequences: a constraints-based approach. Sports Med. 2013 Jun;43(6):385-93.
Zhang J, Wang C, Li X, Fu S, Gu W, Shi Z. Platelet-rich plasma, a biomaterial, for the treatment of anterior talofibular ligament in lateral ankle sprain. Front Bioeng Biotechnol. 2022 Dec 22;10:1073063.