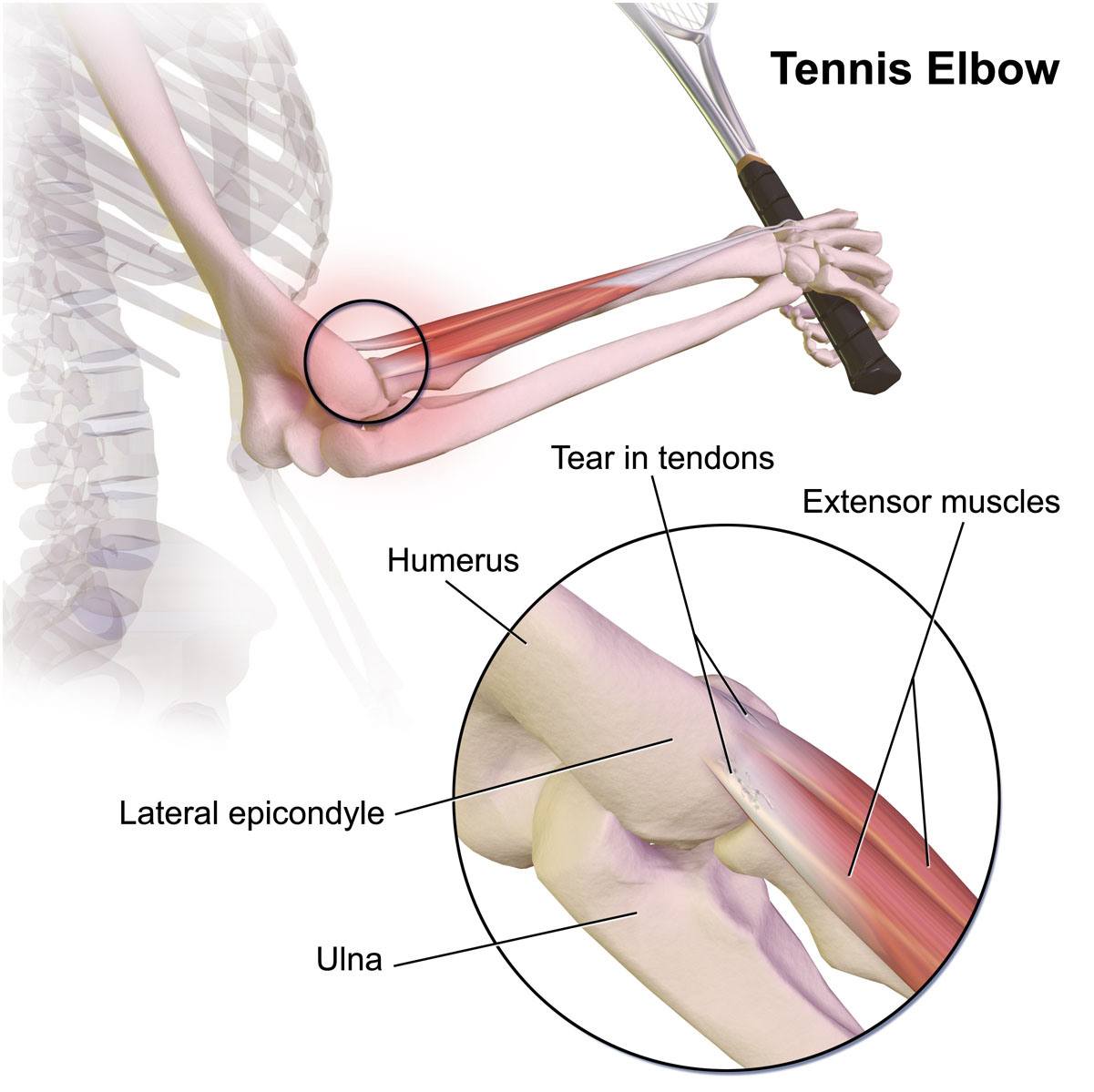
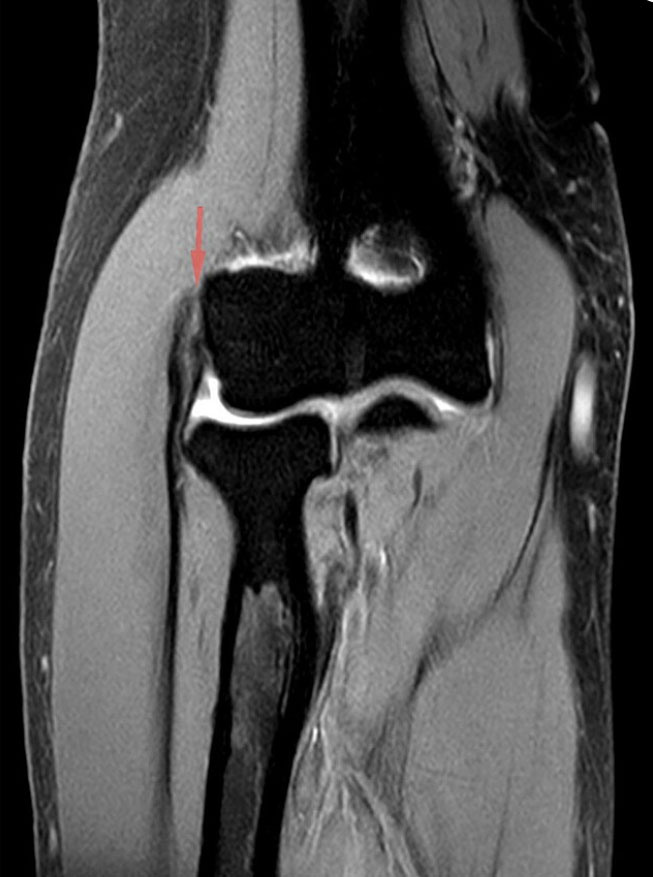
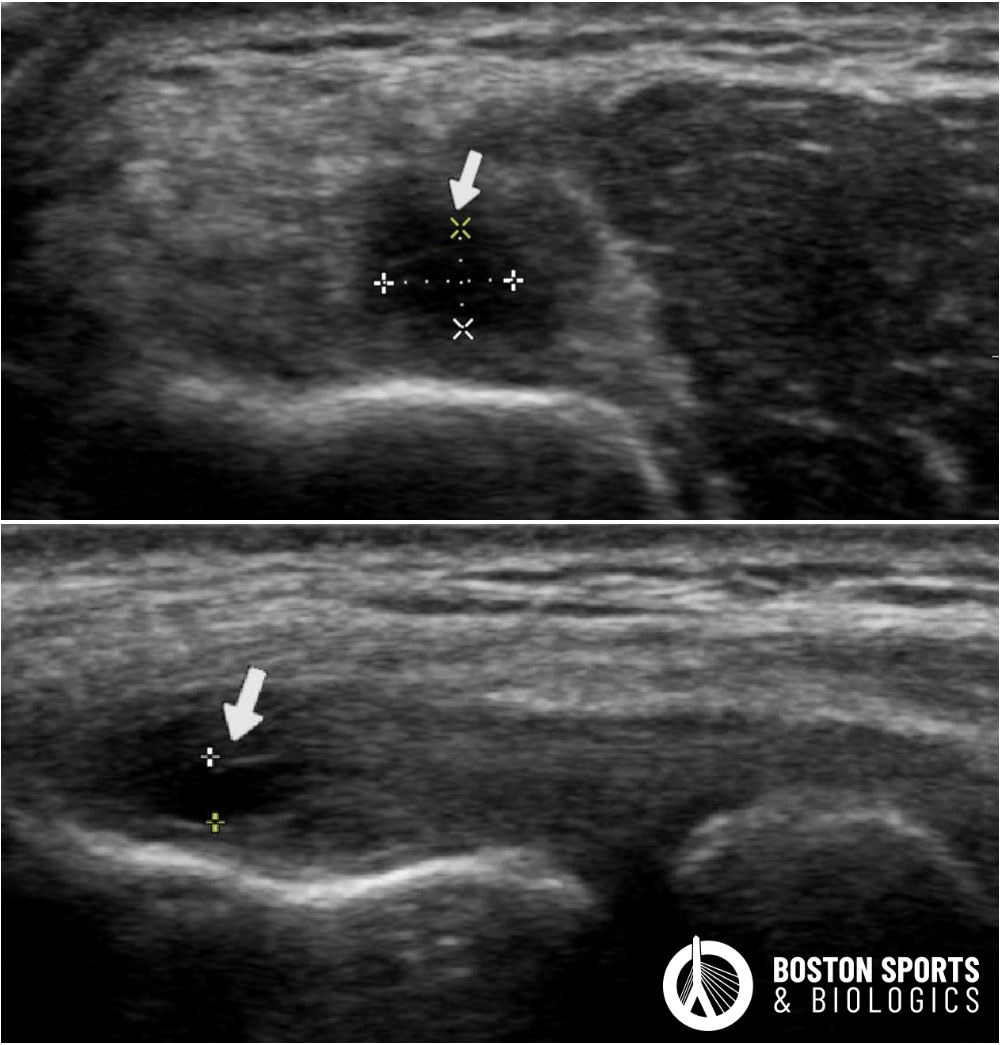
- Corticosteroid injections: Steroids can provide short-term pain relief but should be used with caution due to potential long-term adverse effects. [Hegmann et al, 2013; Johnson et al, 2007; Wolf, 2023].
- In a study by Coombes et al.
in the Journal of the American Medical Association (JAMA), patients
that receive a cortisone injection do worse at the one-year follow-up
than those that receive a placebo injection suggesting that cortisone
injections can help for a few months, but may ultimately inhibit healing
long-term.
- Prolotherapy has been evaluated in several studies, with mixed but generally positive results.
- A systematic review and meta-analysis by Zhu et al. found that hypertonic dextrose prolotherapy (DPT) significantly reduced pain and improved function at 12 weeks compared to active controls.
- Ciftci et al. conducted a double-blind, randomized controlled trial comparing low-dose (5%) and high-dose (15%) dextrose prolotherapy. Both concentrations were more effective than saline in improving pain, handgrip strength and functionality at 12 weeks, with the 15% dextrose group showing superiorresults in handgrip strength and pressure-pain threshold.
- Rabago et al. in a pilot-level randomized controlled trial, demonstrated that prolotherapy with dextrose significantly improved pain and function compared to a wait-and-see approach with a high patient satisfaction and no adverse events.
- Akcay et al. compared dextrose prolotherapy to saline injections and found that prolotherapy significantly improved pain and function as measured at 4 and 12 weeks.
- Platelet-rich plasma (PRP) and autologous blood injections have
conflicting evidence regarding their efficacy with some studies showing benefit and others not. Learn more about PRP HERE.- A systematic review and meta-analysis by Xu et al. found that PRP provides better long-term (≥6 months) improvement in pain and function compared to corticosteroids (CS).[1] Specifically, PRP showed significant improvements in pain and function at the long-term follow-up.
- Oeding et al. highlighted that the efficacy of PRP is influenced by the platelet concentration, with high-dose PRP showing significant pain relief compared to low-dose PRP and other treatments. This suggests that the variability in outcomes may be due to differences in PRP preparation.
- Gosens et al. showed that when comparing PRP to steroids, that PRP to be more effective for tennis elbow.
- Extracorporeal Shock Wave Therapy (ESWT): The evidence for Shock Wave Therapy in the treatment of lateral epicondylitis (tennis elbow) is mixed but generally supports its efficacy, particularly for pain relief and grip strength recovery.
- Liu et al. conducted a network meta-analysis and concluded that ESWT was superior to placebo therapies for both short term and medium-term pain relief and grip strength recovery. ESWT was ranked as the most optimal treatment for grip strength recovery in both short-term and medium-term follow-ups.
- A systematic review and meta-analysis by Yoon et al. found that radial ESWT resulted in improvement pain and grip
strength, although the mean difference in pain scores did not exceed the minimal clinically important difference threshold. The study also noted that ESWT was more effective in patients with symptoms lasting more than six months, but the effects did not last beyond 24 weeks again suggesting short-term benefit.
Operative treatments
Surgery is considered for refractory cases that do not respond to nonoperative measures after 6-12 months:
- Surgical Debridement:
Options include open, arthroscopic, or percutaneous techniques.
Arthroscopic debridement has shown good clinical outcomes and is
associated with radiographic improvements [Hohmann, 2022; Savoie et al, 2010].
- Tenotomy under Ultrasound Guidance using the TENEX device: The evidence for the use of ultrasound-guided tenotomy, including the Tenex system, in the treatment of lateral epicondylitis (tennis elbow) is generally supportive, particularly for patients with refractory symptoms.Learn more about TENEX HERE.
- Koh et al. published the first study on the Tenex device and showed significant improvements in pain and function at the 12 month follow-up. Sonographic assessments revealed reduced tendon thickness, resolved or reduced hypervascularity, and reduced hypoechoic areas. No complications were reported, and 95% of patients expressed satisfaction with the procedure
- A study by Chalian et al. demonstrated that ultrasound-guided tenotomy using the Tenex system significantly improved function in patients with refractory lateral epicondylitis. These improvements were sustained for up to three years, with no reported complications.
- A meta-analysis by Shomal Zadeh et al. found that a tenotomy under ultrasound-guidance significantly alleviated pain and improved function in chronic tendinopathy, including lateral
epicondylitis, with benefits persisting in the short, intermediate, and long term. - Boden et al. compared PRP injections to the Tenex procedure and found both treatments to be effective in improving pain, function, and quality of life, with no significant differences between the two modalities.
- Ang et al. reported long-term benefits of tenotomy under ultrasound-guidance, showing sustained pain relief, functional improvement, and sonographic evidence of tissue healing at 90 months follow-up, with 100% patient satisfaction and no adverse outcomes.
REFERENCES
- Akcay S, Gurel Kandemir N, Kaya T, Dogan N, Eren M. Dextrose Prolotherapy Versus Normal Saline Injection for the Treatment of Lateral Epicondylopathy: A Randomized Controlled Trial. J Altern Complement Med. 2020 Dec;26(12):1159-1168.
- Ang BFH, Mohan PC, Png MA, Allen JC Jr, Howe TS, Koh JSB, Lee BP, Morrey BF. Ultrasonic Percutaneous Tenotomy for Recalcitrant Lateral Elbow Tendinopathy: Clinical and Sonographic Results at 90 Months. Am J Sports Med. 2021 Jun;49(7):1854-1860.
- Boden AL, Scott MT, Dalwadi PP, Mautner K, Mason RA, Gottschalk MB. Platelet-rich plasma versus Tenex in the treatment of medial and lateral epicondylitis. J Shoulder Elbow Surg. 2019 Jan;28(1):112-119.
- Calfee RP, Patel A, DaSilva MF, Akelman E. Management of lateral epicondylitis: current concepts. J Am Acad Orthop Surg. 2008 Jan;16(1):19-29.
- Chalian M, Nacey NC, Rawat U, Knight J, Lancaster T, Deal DN, Pierce J. Ultrasound-guided percutaneous needle tenotomy using Tenex system for refractory lateral epicondylitis; short and long-term effectiveness and contributing factors. Skeletal Radiol. 2021 Oct;50(10):2049-2057.
- Ciftci YGD, Tuncay F, Kocak FA, Okcu M. Is Low-Dose Dextrose Prolotherapy as Effective as High-Dose Dextrose Prolotherapy in the Treatment of Lateral Epicondylitis? A Double-Blind, Ultrasound Guided, Randomized Controlled Study. Arch Phys Med Rehabil. 2023 Feb;104(2):179-187.
- Coombes BK, Bisset L, Brooks P, Khan A, Vicenzino B. Effect of corticosteroid injection, physiotherapy, or both on clinical outcomes in patients with unilateral lateral epicondylalgia: a randomized controlled trial. JAMA. 2013 Feb 6;309(5):461-9.
- Gosens T, Peerbooms JC, van Laar W, den Oudsten BL. Ongoing positive effect of platelet-rich plasma versus corticosteroid injection in lateral epicondylitis: a double-blind randomized controlled trial with 2-year follow-up. Am J Sports Med. 2011 Jun;39(6):1200-8.
Hegmann KT, Hoffman HE, Belcourt RM, Byrne K, Glass L, Melhorn JM, Richman J, Zinni P 3rd, Thiese MS, Ott U, Tokita K, Passey DG, Effiong AC, Robbins RB, Ording JA; American College of Occupational and Environmental Medicine. ACOEM practice guidelines: elbow disorders. J Occup Environ Med. 2013 Nov;55(11):1365-74.
Hohmann E. Editorial Commentary: Arthroscopic Debridement of Tennis Elbow Nonresponsive to Nonoperative Measures Is a Good Option and Clinical Outcomes Are Associated With Radiographic Outcomes. Arthroscopy. 2022 Dec;38(12):3130-3132.
Johnson GW, Cadwallader K, Scheffel SB, Epperly TD. Treatment of lateral epicondylitis. Am Fam Physician. 2007 Sep 15;76(6):843-8.
Keijsers R, de Vos RJ, Kuijer PPF, van den Bekerom MP, van der Woude HJ, Eygendaal D. Tennis elbow. Shoulder Elbow.2019 Oct;11(5):384-392.
Koh JS, Mohan PC, Howe TS, Lee BP, Chia SL, Yang Z, Morrey BF. Fasciotomy and surgical tenotomy for recalcitrant lateral elbow tendinopathy: early clinical experience with a novel device for minimally invasive percutaneous microresection. Am J Sports Med. 2013 Mar;41(3):636-44.
Liu WC, Chen CT, Lu CC, Tsai YC, Liu YC, Hsu CW, Shih CL, Chen PC, Fu YC. Extracorporeal Shock Wave Therapy Shows Superiority Over Injections for Pain Relief and Grip Strength Recovery in Lateral Epicondylitis: A Systematic Review and Network Meta-analysis. Arthroscopy. 2022 Jun;38(6):2018-2034.e12.
McShane JM, Nazarian LN, Harwood MI. Sonographically guided percutaneous needle tenotomy for treatment of common extensor tendinosis in the elbow. J Ultrasound Med. 2006 Oct;25(10):1281-9.
- Oeding JF, Varady NH, Messer CJ, Dines JS, Williams RJ, Rodeo SA. Platelet Concentration Explains Variability in Outcomes of Platelet-Rich Plasma for Lateral Epicondylitis: A High Dose Is Critical for a Positive Response: A Systematic Review and Meta-analysis With Meta-regression. Am J Sports Med. 2025 Jan 27:3635465241303716.
- Rabago D, Lee KS, Ryan M, Chourasia AO, Sesto ME, Zgierska A, Kijowski R, Grettie J, Wilson J, Miller D. Hypertonic dextrose and morrhuate sodium injections (prolotherapy) for lateral epicondylosis (tennis elbow): results of a single-blind, pilot-level, randomized controlled trial. Am J Phys Med Rehabil. 2013 Jul;92(7):587-96.
- Savoie FH 3rd, VanSice W, O'Brien MJ. Arthroscopic tennis elbow release. J Shoulder Elbow Surg. 2010 Mar;19(2 Suppl):31-6.
- Shomal Zadeh F, Shafiei M, Shomalzadeh M, Pierce J, Thurlow PC, Chalian M. Percutaneous ultrasound-guided needle tenotomy for treatment of chronic tendinopathy and fasciopathy: a meta-analysis. Eur Radiol. 2023 Oct;33(10):7303-7320.
- Tosti R, Jennings J, Sewards JM. Lateral epicondylitis of the elbow. Am J Med. 2013 Apr;126(4):357.e1-6.
- Wolf JM. Lateral Epicondylitis. N Engl J Med. 2023 Jun 22;388(25):2371-2377.
- Xu Y, Li T, Wang L, Yao L, Li J, Tang X. Platelet-Rich Plasma Has Better Results for Long-term Functional Improvement and Pain Relief for Lateral Epicondylitis: A Systematic Review and Meta-analysis of Randomized Controlled Trials. Am J Sports Med. 2024 Aug;52(10):2646-2656.
- Zhu M, Rabago D, Chung VC, Reeves KD, Wong SY, Sit RW. Effects of Hypertonic Dextrose Injection (Prolotherapy) in Lateral Elbow Tendinosis: A Systematic Review and Meta-analysis. Arch Phys Med Rehabil. 2022 Nov;103(11):2209-2218.